
GENERATION OF COMPUTERS
Everything that ever existed in this world holds their own generation history as like living beings even the machine has their evolution history they have evolved in a very unique way. There are five generation of computers till date the upcoming paragraph have encountered the specs advantages and the need for the development from one generation to another.
FIRST GENERATION COMPUTERS:
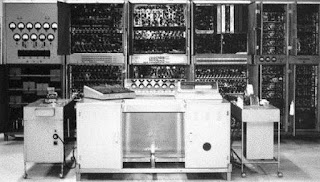 |
| FIRST GENERATION COMPUTERS (1940-1956) |
- These computers were vacuum tubes based machines.
- They used magnetic drums for memory.
- Input were fed into the computers using punched cards.
- They size of these computers were very large and it produced more heat
- They lack in versatility and speed.
- They were more expensive.
SPEED : Fastest computing device of its time.
TECHNOLOGY : Vacuum tubes made up of glass containing filaments when heated generates electrons which helps in amplification and de amplification of signals.
I/p & O/p : Punched card and print out
PROGRAMMING
LANGUAGE : Machine level language
Example:
E D S A C : Electronic delay storage automatic calculator
E D V A C : Electronic discrete variable automatic computer
ADVANTAGES:
- Fastest computing device of their time
- Execute complex mathematical problems in an efficient manner
DISADVANTAGES:
- Large & Bulky
- Difficult to program
- Cannot be transferred from one place to another
- These are special purpose computers
- Generates huge amount of heat and hence prone to hardware faults
SECOND GENERATION COMPUTERS (1956-1963)

- Here the Transistor replaced the bulky vacuum tubes.
- Transistors are smaller than vacuum tubes and have higher operating speed.
- The size of the computer got reduced considerably.
- Manufacturing cost was also very low.
SPEED: Faster than first generation
TECHNOLOGY: Transistor Used to increase the power of incoming signals. It has 3 connections:
BASE : Through which incoming signals are sent
COLLECTOR : Collects amplified signal
EMITTER: Emits amplified signal
I/p & O/p : Punched card and print out
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: Assembly language
Example:
IBM 1401
IBM 1620
ADVANTAGES:
- Fastest computing device of their time
- Easy to program
- Light weight
- Low power consumption
- Low maintenance
- Transferred from one place to another easily
DISADVANTAGES:
- High cost
- Limited to special purpose tasks
- Generates considerable amount of heat
THIRD GENERATION COMPUTERS (1964-1975)

- These computers were based on Integrated Circuits (ICs) Technology.
- A single IC has many transistors, registers and capacitors built on a single thin slice of silicon.
- The size of the computer got further reduced.
- These Computers were small in size, low cost, large memory and processing speed is very high.
SPEED: Fastest computing device of its time
TECHNOLOGY: Integrated Circuits : Also known as micro electronics technology
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: High level language
Example:
IBM 360
Honeywell 6000
ADVANTAGES:
- Computational time was measured in nano seconds
- Requires low power to operate
- Small size
- Installation is very easy
- Able to execute any type of applications
- More reliable & requires less maintenance
- Easily transportable
DISADVANTAGES:
- Storage capacity was very small
- Performance will get degrade while executing large applications
- Cost is very high
- Required to be placed in air conditioned plates
FOURTH GENERATION COMPUTERS (1975-1989)

- It uses very large scale Integrated Circuits (VLSI) built on a single silicon chip called microprocessors .
- These computers are called microcomputers.
- Thus the size of the computer got reduced.
- The personal computer (PC) are comes under the Fourth Generation.
SPEED: Fastest computing device of its time
TECHNOLOGY:
- VLSI Very large scale Integration It leads to the development of GUI, Operating Systems, Various storage devices, I/O devices and LAN
- It has 3 components:
- Microprocessors
- Memory
- I/O Controls
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: High level language
Example:
IBM PC series
Apple Series
ADVANTAGES:
- Very powerful in terms of speed & time
- Storage capacity is very high & it is very fast
- Highly reliable and requires low maintenance
- Provides user friendly environment using GUI(Graphical user
- interface)
- Programs are highly portable
- Highly versatile and requires less power
DISADVANTAGES:
- The soldering of VLSI chips on the wiring board was not an easy task
- Working of these computers depends on instructions given by the programmer
FIFTH GENERATION COMPUTERS(1989-Till date)
- The speed is extremely high in fifth generation computer.
- The concept of Artificial intelligence has been introduced to allow the computer to take its own decision.
- It is still in a developmental stage .
SPEED: Faster of all times
TECHNOLOGY:
- ULSI : Ultra large scale Integration
- It has more than10 million electronic components
- It increases the power & speed of the microprocessor
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE : High level language
Integrated development environment
Example:
Laptop
PDA
ADVANTAGES;
- Fastest & powerful computers till date
- Able to execute a large no of application at very high speed.
- ULSI Technology helps in decreasing the size of computers.
- Multimedia features are available
- Resource sharing is possible & is highly versatile
DISADVANTAGES:
- Lack of human like Intelligence






No comments:
Post a Comment